Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Weisenburger, A.*; Aoto, Kazumi; M ller, G.*; Heinzel, A.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro
ller, G.*; Heinzel, A.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/06
The behaviour of protective oxide layers on P122 and its welds and of ODS steel in LBE is examined under conditions of changing temperatures and oxygen concentrations. P122 teel ( Cr) and its welded joints are exposed to LBE at 550
Cr) and its welded joints are exposed to LBE at 550  C for 4.000 h with oxygen concentrations of 10
C for 4.000 h with oxygen concentrations of 10 and 10
and 10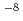 wt% which change every 800 h. It is found that like in case f constant oxygen concentration of 10
wt% which change every 800 h. It is found that like in case f constant oxygen concentration of 10 wt% a protective spinel layer was maintained on P122 and also on its welded joint. Two experiments are conducted on ODS steel, both with temperatures changing from 550 to 650
wt% a protective spinel layer was maintained on P122 and also on its welded joint. Two experiments are conducted on ODS steel, both with temperatures changing from 550 to 650  C and back every 800 h, one experiment with 10
C and back every 800 h, one experiment with 10 the other with 10
the other with 10 wt% oxygen in LBE. Like in the former test with constant emperature at 550
wt% oxygen in LBE. Like in the former test with constant emperature at 550  C no dissolution attack could be observed in experiments with temperature fluctuation. Contrary to this results is the observed dissolution attack on ODS with a onstant temperature of 650
C no dissolution attack could be observed in experiments with temperature fluctuation. Contrary to this results is the observed dissolution attack on ODS with a onstant temperature of 650  C at 10
C at 10 wt% oxygen in which formation of a protective layer was not allowed before reaching 650
wt% oxygen in which formation of a protective layer was not allowed before reaching 650  C LBE temperature.
C LBE temperature.
Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
no abstracts in English
Miyazaki, Akemi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/05
Since it is generally difficult to predict the occurrence of the natural disasters such as earthquakes, a performance management system that always maintains the safety of the structures is required, especially for the critical ones like the nuclear power plants. To realize such a system, it is becoming important to carry out modeling procedures and analyses in detail to capture the real phenomena. Such details are important in understanding the phenomena occurring in the frame structures such as piping systems which are considered to be one of the most weakest and vulnerable parts in the nuclear power plants. The aim of our research is to solve the dynamic behavior, especially the wave propagation phenomena for the piping systems in the nuclear power. The spectral element method is adopted in this work and the formulation considering a shear deformation of a frame element is described. Timoshenko beam theory is introduced for the purpose of this formulation. The validity of the presented element will be shown through the comparisons made with the conventional beam element.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
A hydrogen production system connected to the High-Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) is being designed to be able to produce hydrogen using a nuclear heat of 10 MW supplied by the HTTR. The HTTR hydrogen production system is first connected to a nuclear reactor in the world, hence an mock-up model test is planned to carry out prior to the demonstration test of the HTTR hydrogen production system. In parallel to the mock-up model test, the following tests as an essential problem, a corrosion test of a reforming tube, a permeation test of hydrogen isotopes through a heat exchanger tube, an integrity test of a high-temperature isolation valve, and a performance test of a hydrogen permselective membrane are carried out to obtain detailed data for a safety review and development of analytical codes. This paper describes the present status of the component tests on the R&D of the HTTR hydrogen production system.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakatsuka, Toru
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
In order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the matured Light Water Reactor (LWR) and coming LWR-Mixed Oxide (MOX) technologies, a concept of Innovative Water Reactor for Flexible Fuel Cycle (FLWR) has been investigated in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The concept consists of two parts in the chronological sequence. The first part realizes a high conversion type core concept, which is basically intended to keep the smooth technical continuity from current LWR without significant gaps in technical point of view. The second part represents the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) core concept, which realizes a high conversion ratio over 1.0 being useful for the long-term sustainable energy supply through plutonium multiple recycling based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The key point is that the two core concepts utilize the compatible and the same size fuel assemblies, and hence, the former concept can proceed to the latter in the same reactor system, based flexibly on the fuel cycle circumstances.
 C in HTTR
C in HTTRKawasaki, Kozo; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Tachibana, Yukio; Nakazawa, Toshio; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) achieved a coolant temperature of 950 C at reactor outlet with its rated thermal power of 30MW on April 19, 2004. Achievement of the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950
C at reactor outlet with its rated thermal power of 30MW on April 19, 2004. Achievement of the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950 C makes it possible to extend use of high-temperature gas-cooled reactors beyond the field of electric power generation. Not only highly effective power generation with a high-temperature gas turbine system but also hydrogen production from water without emission of carbon dioxide will be possible utilizing the high temperature heat. This report describes the results of the high-temperature test operation of the HTTR.
C makes it possible to extend use of high-temperature gas-cooled reactors beyond the field of electric power generation. Not only highly effective power generation with a high-temperature gas turbine system but also hydrogen production from water without emission of carbon dioxide will be possible utilizing the high temperature heat. This report describes the results of the high-temperature test operation of the HTTR.
Minehara, Eisuke; Hajima, Ryoichi; Sawamura, Masaru; Nagai, Ryoji; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Iijima, Hokuto; Nishitani, Tomohiro; Kimura, Hideaki*; Oguri, Daiichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2005/05
The JAERI FEL has recently discovered the new FEL lasing of 255fs ultra fast pulse, 6-9% high-efficiency, one gigawatt high peak power, a few kilowatts average power, and wide tunability of medium and far infrared wavelength regions at the same time. Using the new lasing and energy-recovery linac technology, we could extend a more powerful and more efficient free-electron laser (FEL) than 10kW and 25%, respectively, for nuclear industry, pharmacy, medical, defense, shipbuilding, semiconductor industry, chemical industries, environmental sciences, space-debris, power beaming and so on. In order to realize such a tunable, highly-efficient, high average power, high peak power and ultra-short pulse FEL, we need the efficient and powerful FEL driven by the JAERI compact, stand-alone and zero boil-off super-conducting RF linac with an energy-recovery geometry. Our discussions on the FEL will cover the application of non-thermal peeling, cutting, and drilling to decommission the nuclear power plants, and to prevent stress-corrosion cracking in nuclear industry and roadmap for the industrial FELs, the JAERI compact, stand-alone and zero-boil-off cryostat concept and operational experience, the new, highly-efficient, high-power, and ultra fast pulse lasing mode, and the energy-recovery geometry.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Nakatsuka, Toru; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
R&D project to investigate thermal-hydraulic performance in tight-lattice rod bundles for Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) is started at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute in collaboration with power company, reactor vendors, universities since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured LWR technologies. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight-lattice configuration. In this paper, we will show the R&D plan and describe some advances on experimental and analytical studies. The experimental study is performed mainly using large-scale (37-rod bundle) test facility and the analytical one aims to develop a predictable technology for geometry effects such as gap between rods etc. using advanced 3-D two-phase flow simulation methods. Steady-state and transient critical power experiments are conducted with the test facility (Gap width between rods: 1.3mm and 1.0mm) and the experimental data reveal the feasibility of RMWR.
Sato, Haruo
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 0 Pages, 2005/05
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Sato, Haruo
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), Track 8-9 Pages, 2005/05
The anisotropies in the diffusion and activation energies (Ea) of I- and Cs+ ions in compacted smectite and the effect of salinity on the diffusion of both ions were studied. A Na-smectite prepared by ion-exchanging with Na+ ions a Na-bentonite, was used. The diffusion experiments were performed as a function of smectite's dry density, salinity, temperature and diffusion direction to the orientated direction of smectite particles. Considering electrostatic effect from the surface of smectite aggregates and the change in tortuosity on dry density, salinity and diffusion direction, I- ions are presumed to mainly diffuse in interstitial pores, and Cs+ ions are presumed to diffuse in both interlayer and interstitial pores. The change in Ea-values on dry density is considered to be due to the effct of the activity of porewater in addition to the effect of electrostatic effect from smectite surface. Particularly, the diffusion behaviour of Cs+ ions can be explained by considering ion exchange enthalpy between Cs+ and Na+ ions at low-dry density, but it is presumed to be affected by both the decrease in the activity of porewater and the effect of the ion exchange enthalpy at high-dry density.
Izumi, Masanori
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), P. 353, 2005/05
Fugen have been developing Decommissioning Engineering Support system (DEXUS)aimed at planning optimal dismantlement process and carrying out dismantlement work safely and correctly. DEXUS consists of "Decommissioning Plan Support System" and "Dismantlement Support system". We reported about the former sysyem, so we intend to report about the latter system. The main object of dismantlement support system is to ensure safety for wokers collectdismantlement result data and manage genrated wastes during the actual dismatlement works. Now we are develpoing three subsystems such as "Worksite visualization system", "Collecting dismantlement resultsystem" and "Management generated Waste system".
Okamura, Nobuo; Koizumi, Kenji; Washiya, Tadahiro; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 0 Pages, 2005/05
In Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), a commercial scale electrolyzer, whose capacity is 25tHM/y, is been developing to be used in an oxide electrowinning process, a kind of non-aqueous reprocessing process. It has some significant subjects that must be solved before introduced in a commercial reprocessing plant. It developed in JNC has some innovative characteristics, such as cold crucible induction melting (CCIM), to cope with those subjects. But these characteristics make it difficult to arrange the internal components because of a narrow and deep shape of a crucible. So two kinds of analysis systems with computer were constructed to help a design of the internal constitution. One of them is to evaluate the temperature distribution in the crucible and another is to evaluate the shape of deposits. In this study, the internal constitution in the commercial scale electrolyzer was designed by using them finally.
Kawaguchi, Koichi; Namekawa, Takashi; Suzuki, Yoshihiro; Haraguchi, Shingo*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2005/05
The conceptual design study for advanced FBR fuel fabrication system has been performed for the purpose that the feature of small-scale fabrication system in the transition stage from LWR to FBR fuel cycle. On the small-scale of 50 ton heavy metal per year fabrication system, dry type fabrication systems have superior cost performance than the wet type, although waste amount is larger.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Ezure, Toshiki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), P. 432, 2005/05
A compact sodium reactor is designed as a commercialized fast reactor cycle system. A 1/10th scaled water experiment was performed to optimize upper plenum flow in the reactor vessel, because of high flow velocity resulted from the compacted vessel. In the experiment, vortex cavitation was found at the hot leg inlet because of high velocity in the hot leg pipe (9.4m/s in the design). To evaluate inception cavitation condition of the commercialized reactor, we use the cavitation number k in order to consider the difference of system absolute pressures (0.1MPa in experiment and 0.3MPa in design). The minimum pressure at the vortex center will depend on vortex core radius (size of forced vortex region). It is related to axial velocity gradient and fluid viscosity in theory of the Burger's stretched vortex model. We carried out a basic water experiment to investigate the influence of system pressure and fluid viscosity on the vortex cavitation. The cavitation number at the inception of vortex cavitation slightly increased according to the increase of the system absolute pressure. It means that the vortex cavitation occurs easily under higher-pressure condition as compared with the similar condition of cavitation number with lower pressure. However the increase was less than 30% when the system pressure was varied from 0.1 to 0.3MPa. The influence of fluid viscosity was examined by change of fluid temperature. Velocity distribution around the vortex was also measured to see the structure of vortex.
 -ray emission
-ray emissionOtaka, Masahiko; Hirabayashi, Masaru; Ara, Kuniaki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), P. (50439), 2005/05
In order to enhance the maintenance performance of Sodium-Cooled Fast Reactor (SFR), a novel in-sodium imaging technique was proposed for monitoring a deformation or a displacement of in-sodium components or assemblies in primary cooling systems. This technique based on computed tomography using high-energy gamma photons emitted from radioisotopes of sodium (22Na, 24Na) in the primary coolant. Feasibility studies have been performed in order to explore the applicability to typical piping (or vessels). Preliminary analyses exploring measuring time and imaging capability were performed. The results showed that the proposed technique was feasible as a monitoring system of in-sodium components.
Hirabayashi, Masaru; Kondo, Masatoshi*; Ara, Kuniaki; Takahashi, Minoru*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 0 Pages, 2005/05
In Pb-Bi Cooled Direct Contact Boiling Water Small Fast Reactor, PBWFR, a development of a primary loop flow meter is required. Since an electromagnetic flow meter is not better suited to an annular channel geometry such as the primary loop of PBWFR, an ultrasonic flow meter to measure the velocity of Pb-Bi has been developed.An ultrasonic transit-time method is applied to the flow velocity measurement. To evaluate the flow velocity in this method, the sound velocity in Pb-Bi is required. Therefore the sound velocity in Pb-Bi was measured at the temperature range from 187 to 407 C and the experimental correlation equation of the sound velocity was derived. An ultrasonic flow meter which consisted of the high-temperature sensors and the signal processor was developed and manufactured on trial. The piezoelectric element of the sensor was lithium niobate. The sensor was heated up to 500
C and the experimental correlation equation of the sound velocity was derived. An ultrasonic flow meter which consisted of the high-temperature sensors and the signal processor was developed and manufactured on trial. The piezoelectric element of the sensor was lithium niobate. The sensor was heated up to 500 C and the heat resistance was confirmed. The shoe, i.e. the material wetted by Pb-Bi, of the sensor was made from high-chrome steel. The in-water and the in-Pb-Bi tests were performed and the applicability of the ultrasonic flow meter was verified.
C and the heat resistance was confirmed. The shoe, i.e. the material wetted by Pb-Bi, of the sensor was made from high-chrome steel. The in-water and the in-Pb-Bi tests were performed and the applicability of the ultrasonic flow meter was verified.
Nakagiri, Toshio; Kase, Takeshi; Kato, Shoichi; Aoto, Kazumi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2005/05
A new thermochemical and electrolytic hybrid hydrogen production system for sodium cooled FBR has been proposed and developed by JNC. SO3 splitting experiments, theoretical evaluation of thermal efficiency and hydrogen production experiments to substantiate the whole process were performed. Maximum 5 hours stable hydrogen production was obserbed in the hydrogen production experiments.